- Published on
Deploying Unifi Controller on kubernetes
- Authors

- Name
- Giorgos Dimtsas
- @gedim21
Intro
Recently I started migrating all my selfhosted applications from standalone docker containers to kubernetes. The application that gave me the most trouble to migrate was Ubiquiti's Unifi Controller. In this post I'll describe how to deploy the Unifi Controller on kubernetes and access it's console through a Traefik reverse proxy.
Deploying UniFi Controller
Namespace
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: unifi-controller
Just the namespace; nothing special here.
Persistent Volume Claim
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: unifi-longhorn-pvc
namespace: unifi-controller
spec:
storageClassName: longhorn
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
For storage I'm using a Longhorn volume, but of course you can use anything you prefer.
Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: unifi-controller
name: unifi-controller
namespace: unifi-controller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: unifi-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: unifi-controller
spec:
containers:
- image: lscr.io/linuxserver/unifi-controller:latest
name: unifi-controller
resources:
requests:
cpu: '100m'
memory: '1024Mi'
limits:
cpu: '500m'
memory: '2048Mi'
ports:
- name: device-comm
containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
- name: stun
containerPort: 3478
protocol: UDP
- name: default-console
containerPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
- name: secure-redirect
containerPort: 8843
protocol: TCP
- name: http-redirect
containerPort: 8880
protocol: TCP
- name: speedtest
containerPort: 6789
protocol: TCP
- name: unifi-disc
containerPort: 10001
protocol: UDP
- name: unifi-disc-l2
containerPort: 1900
protocol: UDP
volumeMounts:
- name: unifi-controller-config
mountPath: /config
env:
- name: TZ
value: Europe/Athens
volumes:
- name: unifi-controller-config
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: unifi-longhorn-pvc
The deployment is pretty straightforward.
Services
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: unifi-controller
namespace: unifi-controller
spec:
selector:
app: unifi-controller
ports:
- name: stun
port: 3478
protocol: UDP
- name: secure-redirect
port: 8843
protocol: TCP
- name: http-redirect
port: 8880
protocol: TCP
- name: speedtest
port: 6789
protocol: TCP
- name: unifi-disc
port: 10001
protocol: UDP
- name: unifi-disc-l2
port: 1900
protocol: UDP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: unifi-controller-ui
namespace: unifi-controller
annotations:
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/service.serversscheme: https
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/service.serverstransport: unifi-controller-unifi-controller-ui@kubernetescrd
spec:
selector:
app: unifi-controller
ports:
- name: default-console
port: 8443
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: unifi-controller-dev-com
namespace: unifi-controller
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.0.242
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: unifi-controller
ports:
- name: device-comm
port: 8080
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: ServersTransport
metadata:
name: unifi-controller-ui
namespace: unifi-controller
spec:
insecureSkipVerify: true
Defining the services for the controller UI console and for device communication was what gave the most trouble.
Controller UI
The UI console is accessed on port 8443 and requires a HTTPS connection. Furthermore, the console's SSL certificate is self signed.
To accomodate for this, I defined a separate service for the UI console, unifi-controller-ui, and added the traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/service.serversscheme: https annotation so that Traefik will establish a HTTPS connection with the service.
I then created a ServersTransport object with the insecureSkipVerify: true option and added referenced it in the service's traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/service.serverstransport annotation. This makes Traefik ignore the self signed certificate.
Device communication
The service for device communication was more straightforward. I created the unifi-controller-dev-com service, and since I'm using Metallb I created a service of type LoadBalancer and set it's IP with the annotation metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs
After the controller is up and running, I changed the Inform Host in the settings to the same IP, so that the devices will be able to communicate with the controller:
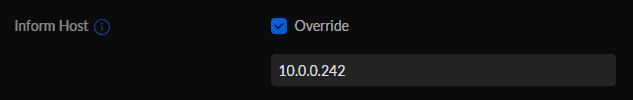
With this, the network devices will be able to be adopted properly by the controller.
Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: unifi-controller
namespace: unifi-controller
annotations:
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/router.entrypoints: websecure
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "lets-encrypt-dns"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- *redacted*
secretName: tls-unifi-ingress-dns
rules:
- host: *redacted*
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: unifi-controller-ui
port:
number: 8443
Finally I created an Ingress object to access the Controller's UI. Since I'm using cert-manager to automatically issue Let's Encrypt certificates, I added the relevant annotations to the object.
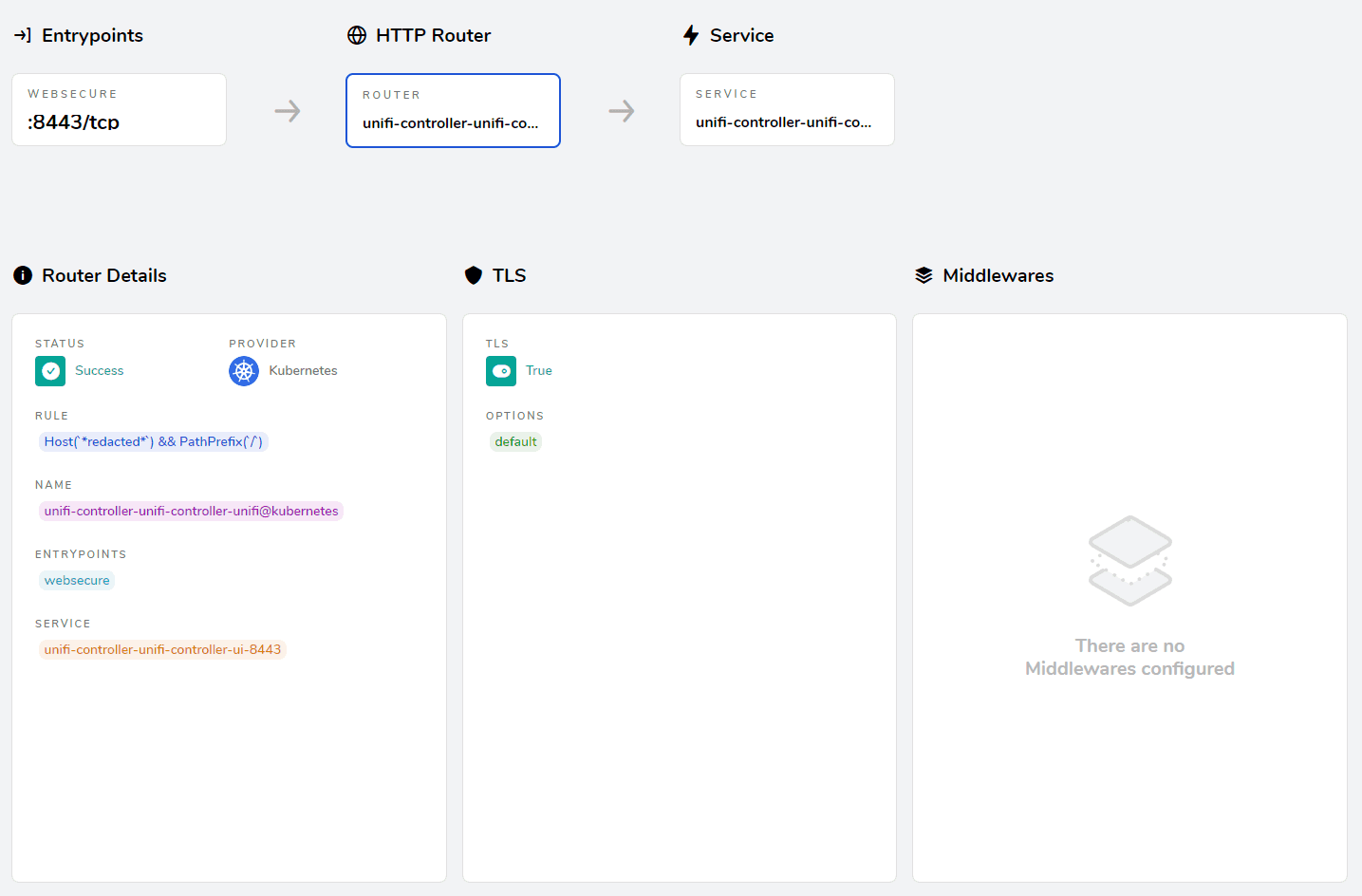
Conclusion
And that's it! It took some troubleshooting but I finally managed to run Unifi Controller on kubernetes! 🎉